pid_t 有符号 16 位、ps 命令、进程号是顺次向下使用、getpid()获取进程 id、getppid()获取父进程 id
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
pid_t getpid(void); //调用进程的进程id
pid_t getppid(void); //调用进程的父进程id
uid_t getuid(void); //调用进程的实际用户ID
uid_t geteuid(void); //调用进程的有效用户id
gid_t getgid(void); //调用进程的实际组id
gid_t getegid(void); //调用进程的有效组id1、实际用户 ID 和实际用户组 ID:标识我是谁。也就是登录用户的 uid 和 gid,比如我的 Linux 以 simon 登录,在 Linux 运行的所有的命令的实际用户 ID 都是 simon 的 uid,实际用户组 ID 都是 simon 的 gid(可以用 id 命令查看)。
2、有效用户 ID 和有效用户组 ID:进程用来决定我们对资源的访问权限。一般情况下,有效用户 ID 等于实际用户 ID,有效用户组 ID 等于实际用户组 ID。当设置-用户-ID(SUID)位设置,则有效用户 ID 等于文件的所有者的 uid,而不是实际用户 ID;同样,如果设置了设置-用户组-ID(SGID)位,则有效用户组 ID 等于文件所有者的 gid,而不是实际用户组 ID。
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
cout << "pid=" << getpid() << endl;
cout << "ppid=" << getppid() << endl;
cout << "uid=" << getuid() << endl;
cout << "euid=" << geteuid() << endl;
cout << "gid=" << getgid() << endl;
cout << "egid=" << getegid() << endl;
return 0;
}
// pid = 102 ppid = 10 uid = 1000 euid = 1000 gid = 1000 egid = 1000#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
pid_t fork(void);
pid_t vfork(void);duplicating 意味着拷贝克隆
fork 后父子进程的区别:fork 返回值不同、pid 不同、ppid
不同、未决信号和文件锁不继承、资源利用量清零
init 进程:是所有进程的祖先进程、PID=1
在 fork 时,缓冲区的内容也会被复制,所以刷新缓冲区操作显得很重要。
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int val = 999;
cout << "start" << endl;
fflush(nullptr);
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid < 0)
{
perror("pid<0");
}
else if (pid == 0) // 子进程
{
cout << val << "子进程 pid = " << pid << " ppid = " << getppid() << endl;
}
else // 父进程
{
cout << val << "父进程 pid = " << getpid() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
/*
start
999父进程 pid = 168
999子进程 pid = 0 ppid = 168
*/进程并发小实例
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
#define RIGHT 3320
#define LEFT 3000
bool check(int val)
{
bool res = true;
for (int i = 2; i < val / 2; i++)
{
if (val % i == 0)
{
res = false;
break;
}
}
return res;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
for (int i = LEFT; i <= RIGHT; i++)
{
int pid = fork();
if (pid == 0)
{
if (check(i))
{
cout << i << endl;
}
return 0;
}
}
return 0;
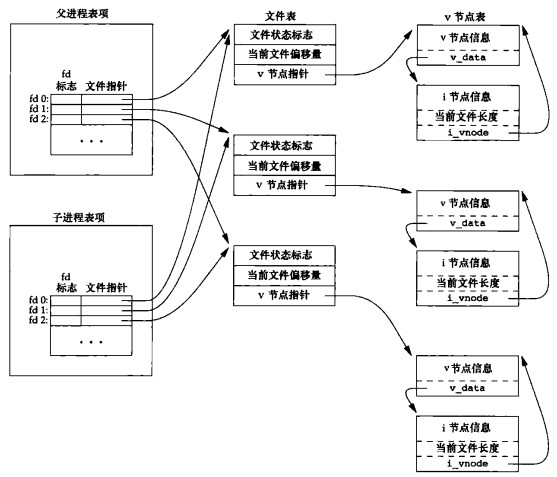
}每个进程有自己的表项,fd 与文件指针的映射表,子进程表项来源于父进程的拷贝。文件指针所指向的文件表是由操作系统管理的,并不会随着 fork 而复制新的文件表。

进程状态
$man ps
PROCESS STATE CODES
Here are the different values that the s, stat and state output specifiers (header "STAT" or "S") will display to describe the state of a process:
D uninterruptible sleep (usually IO)
I Idle kernel thread
R running or runnable (on run queue)
S interruptible sleep (waiting for an event to complete)
T stopped by job control signal
t stopped by debugger during the tracing
W paging (not valid since the 2.6.xx kernel)
X dead (should never be seen)
Z defunct ("zombie 僵尸") process, terminated but not reaped by its parent当子进程结束时,父进程没有结束则子进程会称为僵尸进程,父进程结束时子进程将会称为孤儿进程。 孤儿进程将会由 init 进程接管,释放其资源。
关于 vfork
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
pid_t vfork(void);vfork()会产生一个新的子进程.但是 vfork
创建的子进程与父进程共享数据段,而且由 vfork()创建的
子进程将先于父进程运行.fork()的使用详见百度词条 fork().
vfork()用法与 fork()相似.但是也有区别,具体区别归结为以下 3 点:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
pid_t wait(int *wstatus);//等待进程状态发生变化
pid_t waitpid(pid_t pid, int *wstatus, int options);
// pid:
// > 0 等待进程ID与pid相等的子进程
// 0 等待组ID等于调用进程组ID的任一子进程
// -1 等待任一子进程
// <-1 等待组ID等于pid绝对值的任一子进程
// options:
// WNOHANG 没有子进程结束则立即返回,waitpid变为非阻塞
// WCONTINUED pid指定子进程在停止后已经继续,但状态尚未报告则返回其状态
// WUNTRACED pid指定子进程已处于停止状态,但状态尚未报告则返回其状态
int waitid(idtype_t idtype, id_t id, siginfo_t *infop, int options);
//waitid与waitpid类似waitid 参数


wait 样例
//demo
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
pid_t id = fork();
if (id < 0)
{
return 0;
}
else if (id == 0) // child
{
cout << "child" << endl;
exit(0);
}
int status;
pid_t res_id = wait(&status);
cout<<"child process "<<res_id<<" status changed"<<endl;
cout << "parent" << endl;
cout << res_id << endl;
if (WIFEXITED(status))
{
cout << "正常结束退出码=" << WEXITSTATUS(status) << endl;
cout << "子进程正常终止" << endl;
}
else if (WIFSIGNALED(status))
{
cout << "子进程由信号终止" << endl;
cout << "导致子进程结束的信号码=" << WTERMSIG(status) << endl;
if (WCOREDUMP(status))
{
cout << "产生了core dump文件" << endl;
}
}
if (WIFSTOPPED(status))
{
cout << "子进程已暂停" << endl;
cout << "STOPSIG=" << WSTOPSIG(status) << endl;
}
if (WIFCONTINUED(status))
{
cout << "the child process was resumed by delivery of SIGCONT." << endl;
}
return 0;
}
/*
child
child process 244 status changed
parent
244
正常结束退出码=0
子进程正常终止
*/waitpid 样例
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
pid_t id = fork();
if (id < 0)
{
return 0;
}
else if (id == 0) // child
{
cout << "child" << endl;
exit(0);
}
int status;
pid_t res = waitpid(id, &status, WCONTINUED | WUNTRACED);
cout << "parent" << endl;
return 0;
}
/*
child
parent
*/执行一个文件 execute a file
#include <unistd.h>
extern char **environ;
int execl(const char *pathname, const char *arg, ...
/* (char *) NULL */);
int execlp(const char *file, const char *arg, ...
/* (char *) NULL */);//filename 会直接在环境变量中找path
int execle(const char *pathname, const char *arg, ...
/*, (char *) NULL, char *const envp[] */);
int execv(const char *pathname, char *const argv[]);
int execvp(const char *file, char *const argv[]);
int execvpe(const char *file, char *const argv[],
char *const envp[]);
// 传参从 argv0 开始的用新的进程镜像替换旧的进程镜像
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int res;
fflush(nullptr);
res = execl("/bin/bash", "bash",nullptr); // 新进程替换此进程,pid不变
if (res == -1)
{
perror("execl error");
}
return 0;
}fork、wait 与 exec
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid < 0)
{
perror("pid <0");
exit(0);
}
if (pid == 0)
{
execl("/mnt/c/Users/gaowanlu/Desktop/MyProject/note/testcode/other", "other",nullptr);
exit(0);
}
if (pid > 0)
{
int status;
pid_t res = wait(&status);
cout << res << " is overed" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
/*
other file output "hello world"
gaowanlu@DESKTOP-QDLGRDB:/mnt/c/Users/gaowanlu/Desktop/MyProject/note/testcode$ ./main
hello world
289 is overed
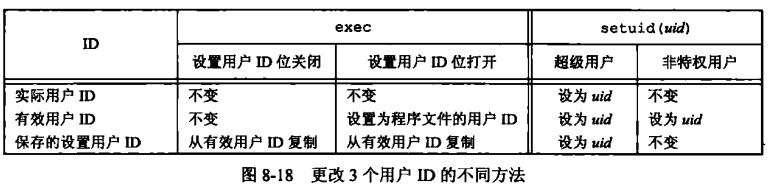
*/用户 ID 与组 ID 有三种,实际 Real ID、有效 Effective Id、保存的设置
Save ID
鉴权的时候看的是有效 ID、realId 是不变的,但有效 ID 是可变的,保存的设置
ID 不一定必须要有
从init到shell的ID变化
r e s
init r:0 e:0 s:0
\
\ fork exec
getey 输入user name r:0 e:0 s:
\
\exec
login进程 输入password r:0 e:0 s:0
check password,/etc/passwd 验证口令,口令不成功则跳到上级
\
\ fork exec
shell r: e: s: 用户自己的相关函数获取用户与组 ID
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
uid_t getuid(void);//r u
uid_t geteuid(void);//e u
gid_t getgid(void);//r g
gid_t getegid(void);//e g设置用户与组 ID
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int setuid(uid_t uid);// sets the effective user ID of the calling process
int seteuid(uid_t euid);//set effective user ID
int setgid(gid_t gid);//sets the effective group ID of the calling process.
int setegid(gid_t egid);// set effective group ID
int setreuid(uid_t ruid, uid_t euid);
int setregid(gid_t rgid, gid_t egid);#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
cout << "uid=" << getuid() << endl;
cout << "euid=" << geteuid() << endl;
cout << "gid=" << getgid() << endl;
cout << "egid=" << getegid() << endl;
return 0;
}
/*
uid=1000
euid=1000
gid=1000
egid=1000
/etc/passwd
gaowanlu:x:1000:1000:,,,:/home/gaowanlu:/bin/bash
*/脚本文件标记
#!/bin/node
//javascript
console.log("hello world");gaowanlu@DESKTOP-QDLGRDB:/$ ls -l main.cpp
-rwxrwxrwx 1 gaowanlu gaowanlu 44 Feb 20 17:09 main.cpp
gaowanlu@DESKTOP-QDLGRDB:/$ ./main.cpp
hello world#!/bin/bash执行命令行
#include <stdlib.h>
int system(const char *command);
//execl("/bin/sh", "sh", "-c", command, (char *) NULL);
//过程起始就是 fork exec wait 组合使用效果#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
system("node");
return 0;
}
10 tty1 S 0:00 \_ -bash
140 tty1 S 0:00 \_ ./main
141 tty1 S 0:00 \_ sh -c node
142 tty1 Sl 0:00 \_ node相关重要函数,进程结束时将进程相关 acct 信息追加到 filename 指定文件中,但不同的系统会有不同,有的不支持 acct(CONFORMING TO SVr4, 4.3BSD (but not POSIX).)
#include <unistd.h>
//switch process accounting on or off
int acct(const char *filename);
struct acct {
char ac_flag; /* Accounting flags */
u_int16_t ac_uid; /* Accounting user ID */
u_int16_t ac_gid; /* Accounting group ID */
u_int16_t ac_tty; /* Controlling terminal */
u_int32_t ac_btime; /* Process creation time
(seconds since the Epoch) */
comp_t ac_utime; /* User CPU time */
comp_t ac_stime; /* System CPU time */
comp_t ac_etime; /* Elapsed time */
comp_t ac_mem; /* Average memory usage (kB) */
comp_t ac_io; /* Characters transferred (unused) */
comp_t ac_rw; /* Blocks read or written (unused) */
comp_t ac_minflt; /* Minor page faults */
comp_t ac_majflt; /* Major page faults */
comp_t ac_swaps; /* Number of swaps (unused) */
u_int32_t ac_exitcode; /* Process termination status
(see wait(2)) */
char ac_comm[ACCT_COMM+1];
/* Command name (basename of last
executed command; null-terminated) */
char ac_pad[X]; /* padding bytes */
};
enum { /* Bits that may be set in ac_flag field */
AFORK = 0x01, /* Has executed fork, but no exec */
ASU = 0x02, /* Used superuser privileges */
ACORE = 0x08, /* Dumped core */
AXSIG = 0x10 /* Killed by a signal */
};#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/acct.h>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
if(-1 == acct("./temp.txt")){
cout << strerror(errno) << endl;
}
return 0;
}怎样获取登录用户名,可以使用 getpwuid(getuid())
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <pwd.h>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
const struct passwd *pwd = getpwuid(getuid());
cout << pwd->pw_name << endl; // gaowanlu
return 0;
}但有时同一个 uid 可能对应多个 username
#include <unistd.h>
char *getlogin(void);#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
const char *res = getlogin();
if (res == nullptr)
{
cout << "res==null " << strerror(errno) << endl;
}
else
{
cout << res << endl;
}
return 0;
}
// ls: cannot access '/etc/adm': No such file or directory
// ubuntu wsl2学过操作系统理论,可以知道进程调度是有优先级的
相关重要函数
//change process priority
#include <unistd.h>
int nice(int inc);//使用nice只对本进程友好值修改不影响其他进程
//成功返回inc,否则返回-1
//get/set program scheduling priority
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/resource.h>
int getpriority(int which, id_t who);
int setpriority(int which, id_t who, int prio);
/*
which: PRIO_PROCESS表进程、PRIO_PGRP表进程组、PRIO_USER表用户ID
which与who关系可以查阅 apue p221
*/进程的默认优先级一般为友好值 NZERO、可以用 sysconf(_SC_NZERO)查看
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
cout << sysconf(_SC_NZERO) << endl; // 20
return 0;
}相关函数,获取进程时间,时间有三种 墙上时钟时间、用户 CPU 时间、系统 CPU 时间
#include <sys/times.h>
clock_t times(struct tms *buf);
struct tms
{
clock_t tms_utime; /* user time */
clock_t tms_stime; /* system time */
clock_t tms_cutime; /* user time of children */
clock_t tms_cstime; /* system time of children */
};样例
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/times.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
clock_t now1 = times(nullptr);
cout << "每秒钟" << sysconf(_SC_CLK_TCK) << "滴答" << endl;
sleep(2);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++)
{
cout << i << j << endl;
}
}
struct tms t;
clock_t now2 = times(&t);
long v = sysconf(_SC_CLK_TCK);
cout << "sum=" << ((now2 - now1) / v) << "s" << endl;
cout << "user time=" << t.tms_utime << endl;
cout << "system time=" << t.tms_stime << endl;
cout << "user time of children=" << t.tms_cutime << endl;
cout << "system time of children=" << t.tms_cstime << endl;
return 0;
}
/*
sum=2s //这里面包含sleep的2s
user time=0
system time=1
user time of children=0
system time of children=0
*/