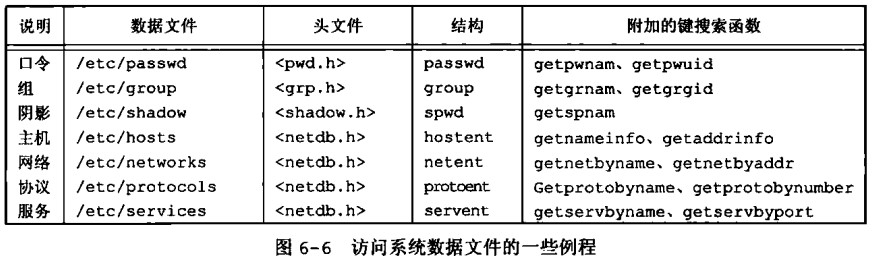
/etc/passwd 文件的大致内容格式为
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
daemon:x:1:1:daemon:/usr/sbin:/usr/sbin/nologin
bin:x:2:2:bin:/bin:/usr/sbin/nologin
sys:x:3:3:sys:/dev:/usr/sbin/nologin//pwd.h
/* A record in the user database. */
struct passwd
{
char *pw_name; /* Username. */
char *pw_passwd; /* Hashed passphrase, if shadow database
not in use (see shadow.h). */
__uid_t pw_uid; /* User ID. */
__gid_t pw_gid; /* Group ID. */
char *pw_gecos; /* Real name. */
char *pw_dir; /* Home directory. */
char *pw_shell; /* Shell program. */
};获取口令函数,获取用户详细信息
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <pwd.h>
struct passwd *getpwnam(const char *name);//根据登录用户名获取
struct passwd *getpwuid(uid_t uid);//根据uid获取
int getpwnam_r(const char *name, struct passwd *pwd,
char *buf, size_t buflen, struct passwd **result);
int getpwuid_r(uid_t uid, struct passwd *pwd,
char *buf, size_t buflen, struct passwd **result);如果只是获取登录名或用户 ID
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <pwd.h>
struct passwd *getpwent(void);//第一次调用打开/etc/passwd文件 getpwent为获取下一项 到文件末尾返回nullptr
void setpwent(void);//读写地址指向文件开头
void endpwent(void);//关闭打开文件
//demo 使用getpwent可是实现getpwnam
#include <pwd.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
struct passwd *ptr = getpwent();
while (ptr)
{
cout << ptr->pw_name << " " << ptr->pw_passwd << endl;
ptr = getpwent();
}
setpwent();
endpwent();
return 0;
}无回显输入内容
#include <unistd.h>
char *getpass(const char *prompt);#include <crypt.h>
char * crypt(const char *phrase, const char *setting);
phrase 要加密的明文
setting 密钥
支持 DES Blowfish MD5加密,具体加密算法根据setting内容长度而定文件格式
gaowanlu:$6$U4XjogvH/T4Uh3AL$rwI2004K.KLw13OAAbHY6.pWWa1fSowYlyUheRjNWS3qvoMQl0xIgZS7yB0sLDHRYJ2SJZM9g0WIEBA2V938T/:18852:0:99999:7:::
mysql:!:19295:0:99999:7:::
fwupd-refresh:*:19302:0:99999:7:::/* A record in the shadow database. */
struct spwd
{
char *sp_namp; /* Login name. */
char *sp_pwdp; /* Hashed passphrase. 加密口令 */
long int sp_lstchg; /* Date of last change. 上次更改口令以来经过的时间*/
long int sp_min; /* Minimum number of days between changes. 经多少天后允许修改 */
long int sp_max; /* Maximum number of days between changes. 要求更改尚余天数 */
long int sp_warn; /* Number of days to warn user to change
the password. 超期警告天数 */
long int sp_inact; /* Number of days the account may be
inactive. 账户不活动之前尚余天数 */
long int sp_expire; /* Number of days since 1970-01-01 until
account expires. 账户超期天数 */
unsigned long int sp_flag; /* Reserved. 保留 */
};查看 shadow 文件相关函数
//使用方式与口令相关函数类似
/* General shadow password file API */
#include <shadow.h>
struct spwd *getspnam(const char *name);
struct spwd *getspent(void);
void setspent(void);
void endspent(void);
//还有其他API更多可以看man//demo
#include <iostream>
#include <shadow.h>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
struct spwd *ptr = getspnam("gaowanlu");
cout << ptr->sp_namp << " " << ptr->sp_pwdp << endl;
// gaowanlu $6$U4XjogvH/T4Uh3AL$rwI2004K.KLw13OAAbHY6.pWWa1fSowYlyUheRjNWS3qvoMQl0xIgZS7yB0sLDHRYJ2SJZM9g0WIEBA2V938T/
return 0;
}/etc/group 格式
root:x:0:
daemon:x:1:
bin:x:2:
sys:x:3:
adm:x:4:syslog,gaowanlu
tty:x:5:syslog/* The group structure. */
struct group
{
char *gr_name; /* Group name. 组名*/
char *gr_passwd; /* Password 加密口令. */
__gid_t gr_gid; /* Group ID. 数值组ID */
char **gr_mem; /* Member list. 指向各用户名指针的数组 */
};相关函数
//使用方法与上面都很类似
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <grp.h>
struct group *getgrnam(const char *name);
struct group *getgrgid(gid_t gid);
int getgrnam_r(const char *name, struct group *grp,
char *buf, size_t buflen, struct group **result);
int getgrgid_r(gid_t gid, struct group *grp,
char *buf, size_t buflen, struct group **result);
struct group *getgrent(void);
void setgrent(void);
void endgrent(void);//demo
#include <iostream>
#include <grp.h>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
struct group *grp = getgrgid(1);
cout << grp->gr_gid << " " << grp->gr_name << " " << grp->gr_passwd << endl;
return 0;
}获取和设置附属 ID 相关函数
//根据进程所属用户而言
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
//size不能大于NGROUPS_MAX
int getgroups(int size, gid_t list[]);//成功返回附属组id数量,出错返回-1
#include <grp.h>
int setgroups(size_t size, const gid_t *list);
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <grp.h>
int initgroups(const char *user, gid_t group);//这两个成功返回0,出错返回-1
//The initgroups() function initializes the group access list by reading the group database /etc/group and using all groups of which user is a member. The additional group group is also added to the list.
//initgroups读取/etc/group 并且会调用setgroups
使用方法都与前面三个类似
登录账户记录:utmp 文件记录当前登录到系统的各个用户,wtmp 文件跟踪各个登录和注销时间,struct utmp 中有登录的用户名,登录的秒数等等,可以看 man utmp 通常在/var/log /var/run/ /var/adm 文件夹下
系统标识:获取主机和操作系统相关信息
//$ uname
//Linux
#include <sys/utsname.h>
int uname(struct utsname *buf);//出错返回负值
struct utsname
{
char sysname[]; /* Operating system name (e.g., "Linux") */
char nodename[]; /* Name within "some implementation-defined
network" */
char release[]; /* Operating system release (e.g., "2.6.28") */
char version[]; /* Operating system version */
char machine[]; /* Hardware identifier */
#ifdef _GNU_SOURCE
char domainname[]; /* NIS or YP domain name */
#endif
};
#include <unistd.h>//进程所属主机的主机名获取和设置
int gethostname(char *name, size_t len);
int sethostname(const char *name, size_t len);
//demo
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
char buffer[_SC_HOST_NAME_MAX];
gethostname(buffer, sizeof(buffer));
cout << buffer << endl; // DESKTOP-QDLGRDB
return 0;
}UTC 时间是从 1970 年 1 月 1 日 00:00:00 以来经过的秒数,使用 time_t 数据类型标识
#include <iostream>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
time_t now;
time_t res = time(&now);
cout << now << " " << res << endl; // 1668219159 1668219159
//若失败则返回-1
return 0;
}clock_gettime 函数用于获取指定时钟的时间
#include <time.h>
int clock_getres(clockid_t clk_id, struct timespec *res);//获取时钟精度
int clock_gettime(clockid_t clk_id, struct timespec *tp);
//使用适当的特权更改时钟值,有些时钟是不能修改的
int clock_settime(clockid_t clk_id, const struct timespec *tp);
//clk_id: CLOCK_REALTIME实时系统时间
//CLOCK_MONOTONIC 不带负跳数的实时系统时间
//CLOCK_PROCESS_CPUTIME_ID 调用进程的CPU时间
//CLOCK_THREAD_CPUTIME_ID 调用线程的CPU时间
struct timespec
{
time_t tv_sec; /* seconds秒 */
long tv_nsec; /* nanoseconds纳秒 */
};struct tm *gmtime(const time_t *timep);
struct tm *gmtime_r(const time_t *timep, struct tm *result);
struct tm *localtime(const time_t *timep);
struct tm *localtime_r(const time_t *timep, struct tm *result);
struct tm
{
int tm_sec; /* Seconds (0-60) */
int tm_min; /* Minutes (0-59) */
int tm_hour; /* Hours (0-23) */
int tm_mday; /* Day of the month (1-31) */
int tm_mon; /* Month (0-11) */
int tm_year; /* Year - 1900 */
int tm_wday; /* Day of the week (0-6, Sunday = 0) */
int tm_yday; /* Day in the year (0-365, 1 Jan = 0) */
int tm_isdst; /* Daylight saving time */
};time_t mktime(struct tm *tm);#include <time.h>
size_t strftime(char *s, size_t max, const char *format,
const struct tm *tm);关于 format

//demo
#include <iostream>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
time_t now;
time(&now);
tm *t = localtime(&now);
if (t)
{
char buffer[124];
if (strftime(buffer, 124, "%Y %B %d", t))
{
cout << buffer << endl; // 2022 November 12
}
}
return 0;
}#include <time.h>
char *strptime(const char *s, const char *format, struct tm *tm);
//返回值 指向上一次解析的字符的下一个字符的指针、否则返回NULLformat,详细内容还得看 man 手册

#include <iostream>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
tm t;
const char *str_format = "%Y %m %d";
const char *str = "2022 11 12";
strptime(str, str_format, &t);
cout << t.tm_year + 1900 << endl; // 2022
cout << t.tm_mon << endl; // 10 [0-11]
cout << t.tm_mday << endl; // 12
return 0;
}