//man fstatat
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int stat(const char *pathname, struct stat *statbuf);
int fstat(int fd, struct stat *statbuf);//以fd为文件描述符
int lstat(const char *pathname, struct stat *statbuf);
#include <fcntl.h> /* Definition of AT_* constants */
#include <sys/stat.h>
int fstatat(int dirfd, const char *pathname, struct stat *statbuf,
int flags);//根据dirfd位置提供pathname#include <unistd.h>
int access(const char *pathname, int mode);
#include <fcntl.h> /* Definition of AT_* constants */
#include <unistd.h>
int faccessat(int dirfd, const char *pathname, int mode, int flags);
//mode可以提供 R_OK W_OK X_OK unistd.h#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
mode_t umask(mode_t mask);#include <sys/stat.h>
int chmod(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);
int fchmod(int fd, mode_t mode);
#include <fcntl.h> /* Definition of AT_* constants */
#include <sys/stat.h>
int fchmodat(int dirfd, const char *pathname, mode_t mode, int flags);也称为 t 位,不用太了解,请求分页的一种优化方式
用于修改文件的用户 ID 和组 ID
#include <unistd.h>
int chown(const char *pathname, uid_t owner, gid_t group);
int fchown(int fd, uid_t owner, gid_t group);
int lchown(const char *pathname, uid_t owner, gid_t group);
#include <fcntl.h> /* Definition of AT_* constants */
#include <unistd.h>
int fchownat(int dirfd, const char *pathname,
uid_t owner, gid_t group, int flags);stat 结构体中成员 st_size 表示以字节位单位的文件的长度,此字段指对普通文件、目录文件、符号链接有意义
复制一个含有空洞的文件,新文件中的空洞占用实际的空间
open 时指定 O_TRUNC,可以使用 truncate 和 ftruncate 函数截断文件
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int truncate(const char *path, off_t length);
int ftruncate(int fd, off_t length);
//只保留前length字节,后面的删除,若length大于原来的实际大小,则会产生空洞目录块里存目录项,目录项里面有文件名和 i 节点编号的元组,i 节点编号指向之际的 i 节点,一个 i 节点指向多个数据块
通常创建硬链接要求二者在同一个文件系统下,也就是有多个目录项中的 i 节点编号指向了相同的 i 节点,也正是这样形成了可以再命名新的名字是被允许的,因为二者的目录项里面存储的文件名不同
用于创建与删除硬链接,当 i 节点的引用为 0 时,才会真的删除数据文件
#include <unistd.h>
int link(const char *oldpath, const char *newpath);
#include <fcntl.h> /* Definition of AT_* constants */
#include <unistd.h>
int linkat(int olddirfd, const char *oldpath,
int newdirfd, const char *newpath, int flags);
#include <unistd.h>
int unlink(const char *pathname);
#include <fcntl.h> /* Definition of AT_* constants */
#include <unistd.h>
int unlinkat(int dirfd, const char *pathname, int flags);#include <stdio.h>
int rename(const char *oldpath, const char *newpath);
#include <fcntl.h> /* Definition of AT_* constants */
#include <stdio.h>
int renameat(int olddirfd, const char *oldpath,
int newdirfd, const char *newpath);
int renameat2(int olddirfd, const char *oldpath,
int newdirfd, const char *newpath, unsigned int flags);软链接,避开了硬链接通常要求链接和文件位于同一文件系统中,只有超级用户才能创建指向目录的硬链接
什么意思,跟随符号链接也就是会去处理其链接的实际文件,不跟随符号链接也就是会处理符号链接本身,因为其也是一个文件,某些函数是否跟随可查搜索
#include <unistd.h>
int symlink(const char *target, const char *linkpath);
#include <fcntl.h> /* Definition of AT_* constants */
#include <unistd.h>
int symlinkat(const char *target, int newdirfd, const char *linkpath);
//前者为真实文件 后者是创建的软连接路径#include <unistd.h>
ssize_t readlink(const char *pathname, char *buf, size_t bufsiz);
#include <fcntl.h> /* Definition of AT_* constants */
#include <unistd.h>
ssize_t readlinkat(int dirfd, const char *pathname,
char *buf, size_t bufsiz);用于更改文件访问和修改时间
#include <fcntl.h> /* Definition of AT_* constants */
#include <sys/stat.h>
int utimensat(int dirfd, const char *pathname,
const struct timespec times[2], int flags);
int futimens(int fd, const struct timespec times[2]);某些函数对文件操作,其相关时间被修改,然后使用这些函数改回原来的时间是被允许的
用于创建目录和删除空目录
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int mkdir(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);
#include <fcntl.h> /* Definition of AT_* constants */
#include <sys/stat.h>
int mkdirat(int dirfd, const char *pathname, mode_t mode);#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
DIR *opendir(const char *name);
DIR *fdopendir(int fd);
#include <dirent.h>
struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dirp);//返回目录中的第一个目录项,取决于location位置
struct dirent {
ino_t d_ino; /* Inode number */
off_t d_off; /* Not an offset; see below */
unsigned short d_reclen; /* Length of this record */
unsigned char d_type; /* Type of file; not supported
by all filesystem types */
char d_name[256]; /* Null-terminated filename */
};
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
int closedir(DIR *dirp);//关闭文件夹
void rewinddir(DIR *dirp);//reset directory stream
long telldir(DIR *dirp);//return current location in directory stream
void seekdir(DIR *dirp, long loc);
//set the position of the next readdir() call in the directory stream.更改当前工作目录与获取当前工作目录,每个进程有自己的当前工作目录
#include <unistd.h>
int chdir(const char *path);
int fchdir(int fd);//fd必须为文件目录的文件描述符
#include <unistd.h>
char *getcwd(char *buf, size_t size);
char *getwd(char *buf);
char *get_current_dir_name(void);进行文件名模式匹配
#include <glob.h>
int glob(const char *pattern, int flags,
int (*errfunc) (const char *epath, int eerrno),
glob_t *pglob);
void globfree(glob_t *pglob);设备由主、次设备号标识
//如果是设备,可以使用stat获取结构体struct stat信息,使用
major(info.st_dev)获取主设备号
minor(info.st_dev)获取次设备号
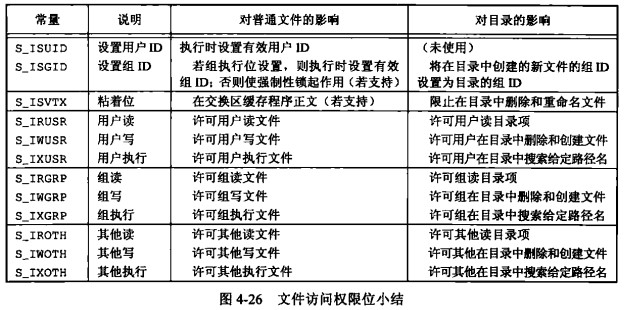
S_IRWXU=SIRUSR|S_IWUSR|S_IXUSR
S_IRWXG=S_IRGRP|S_IWGRP_S_IXGRP
S_IRWXO=S_IROTH|S_IWOTH|S_IXOTH